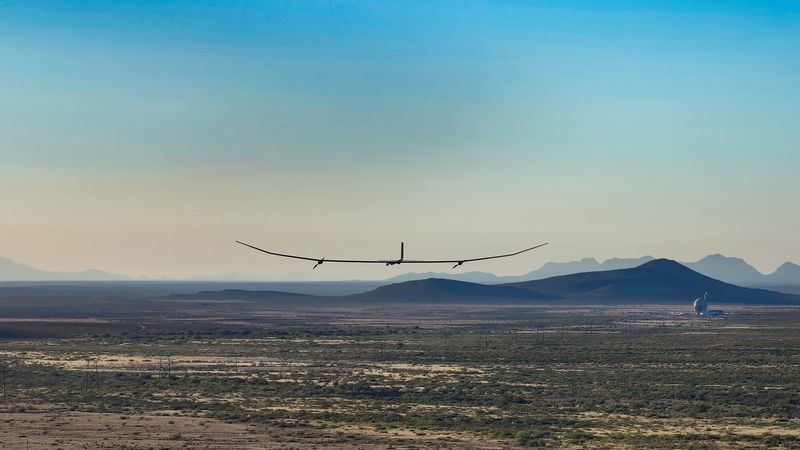
A new spy drone with an unusually slender design has been cruising through Earth’s stratosphere in its latest test flights. With the potential to stay airborne for several months, perhaps a whole year, the novel aircraft is aiming to shake up the satellite game.
It’s known as PHASA-35, an ultra-lightweight, solar-electric High Altitude Pseudo-Satellite (HAPS) Unmanned Aerial System (UAS) that’s been developed by British missile maker BAE Systems.
In its latest test flight, the drone was launched for Spaceport America in New Mexico at an undisclosed time in late 2024. It flew for 24 hours, exceeding an altitude of meters 20,110 metres (66,000 feet), while carrying a payload that was twice as heavy as its previous flights.
With a 35-meter (almost 115-foot) wingspan, the experimental drone consists of an extremely slim body that would struggle to contain a cockpit for a GI Joe figurine. Fortunately, it doesn’t need to be crewed by a living, breathing person. Instead, it’s remotely controlled by a human autopilot operator.

PHASA-351’s role will eventually be to provide militaries, governments, and commercial customers with “ultra-long endurance intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance, as well as security.” Nothing too nefarious, let's hope.
It’s powered by an onboard solar power generator and storage capacity. This self-sufficient and renewable power supply could potentially allow the machine to stay airborne for up to a year, says BAE.
If and when that’s achieved, it would smash the world record for the longest airborne flight, currently held by Robert Timm and John Cook for flying in a plane for almost 65 days in 1958-1959. In 2022, a solar-powered drone called Zephyr came close to snatching the record, but it ended up crashing down after 64 days, 18 hours, and 26 minutes – less than 4 hours away from breaking the record.
Records aside, the potential for PHASA-351 to remain airborne for months at a time makes it a possible alternative to satellites, which can be costly to launch, adapt, and maintain.
“The UAS also has the potential to be used in the delivery of communications networks including 5G, as well as provide other services, such as disaster relief and border protection, at a fraction of the cost of satellites,” BAE says on their website.
“Without the need to refuel, PHASA-35 is able to operate over an area of interest for several months, pushing the boundaries of aviation technology,” the company adds.